GRANT THORNTON TECHNOLOGIES
IT STRATEGY & DATA & ANALYTICS
GRANT THORNTON TECHNOLOGIES
IT STRATEGY & DATA & ANALYTICS
Auditing is an assessment of a system, process, project or product of an organization.
The audit makes it possible to measure a difference between a given benchmark and the observed reality and will also take into account the good business practices in force in the company. Its goal is to assess the evidence to determine whether IS and related resources adequately protect an organization’s information assets.
OVERVIEW OF RISKS COVERED BY AN AUDIT IS
- Risks related to organization and management policies
- Risks associated with the separation of functions
- Risks associated with logical access controls
- Risks related to physical access control
- Risks associated with controlling the development and modifications of programs and systems
- Risks related to business continuity
- Risks associated with IT processing
- Risks associated with users
WHAT ARE THE TOPICS COVERED BY THE SI AUDIT?
The IS audit is cross-functional and affects all the processes of the Information Systems Department. On the other hand, for reasons of time and budget, most IS audits focus on a thematic approach. These themes are generally the following :
- IS management audit
- IT production audit
- Audit of user support and fleet management
- The audit of the “Studies” function
- The security audit
- Audit of computer applications
- Audit of IT projects
- The audit of specific IT markets
SOME CHECKPOINTS
- IS management audit
General control points:
-
- Roles and positioning of IT in the organization
- Strategic planning
- IT budgets and costs
- IT performance measurement and monitoring
- Organization and structure of the IT department
Referencials : COBIT 5, CGEIT
- IT production audit
General control points:
-
- Organization of the production function
- Hardware and software architectures
- Deliveries in production
- Operation and incident management
- Backup and recovery procedure
- Basic hardware and software maintenance
Referencials : ITIL, CMMI, ISO 20000
- Security audit
General control points:
-
- Governance, policy and procedures in place in terms of security
- Security organization
- Classification and controls of assets
- Staff safety
- Communications and operations management
- Management of usernames and passwords
- Access control
- Security requirements in the development and maintenance of systems
Referencials : ISO 27001, ISO 27002, CISSP, CRISC
- Audit of computer applications
General control points:
-
- Application Policy
- Analysis of the risks associated with the application
- Analysis of the risks associated with the IT function
- Suitability of the application to the needs
- Analysis of application performance and profitability
- Analysis of the scalability of the application
Referencials : ITIL
- Audit of user support and fleet management
General control points :
-
- Support function: reliability, security, efficiency and performance
- Management of the hardware and software fleet: reliability, security, efficiency and performance
Referencials : ITIL
- The audit of the “Studies” function
General control points :
-
- Piloting
- Operational activities: specific developments
Referencials : ITIL
- Audit of IT projects
General control points :
-
- Project objectives and challenges
- Opportunity studies and expression of needs
- Planning
- Steering bodies
- Methods and tools
- Quality
- General design and analysis
- Detailed design
- Development, realization or configuration
- Tests and recipes
- Change management and implementation
- Documentation
- Structures put in place during the project
- Management of changes
- Production
Referencials : PMP, Prince 2, ITIL
- The audit of specific IT markets
General control points :
-
- Technical assistance market studies (AMOA)
- Market studies for the acquisition of IT services on the basis of a fixed price
- Study of outsourcing or third-party application maintenance (TMA) markets
The purpose of a BRP is to establish procedures for recovering the computer system after an incident.
We help you to:
- Maximize the efficiency of emergency operations through an established plan that includes the following phases :
- Notification / Activation phase to detect and assess damage and to activate the plan.
- Recovery phase to restore temporary operations and recover damage done to the original system.
- Reconstitution phase to bring the system processing possibilities back to normal operation.
- Identify the activities, resources, and procedures required to monitor the computer system and deal with conditions during system interruptions deemed to be prolonged by the BIA (Business Impact Analysis).
- Assign responsibilities to responsible persons and provide the necessary recommendations to recover the computer system for periods deemed extended by the system by the BIA (Business Impact Analysis).
- Coordinate with the responsible people who will be involved in emergency planning strategies.
- Also coordinate with maintenance providers who will participate in emergency planning strategies.
WHAT IS DATA ANALYSIS ?
Data analysis software commonly known as CAAT (Computer Assisted Audit Technique) or TAAO in french is used on a PC like a “super Excel”. TAAO is the practice of using computers to automate the process of auditing or analyzing data. TAAO has become synonymous with data analysis.
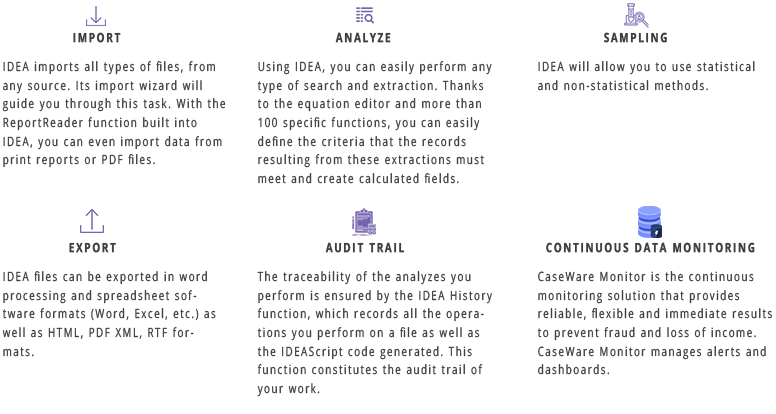
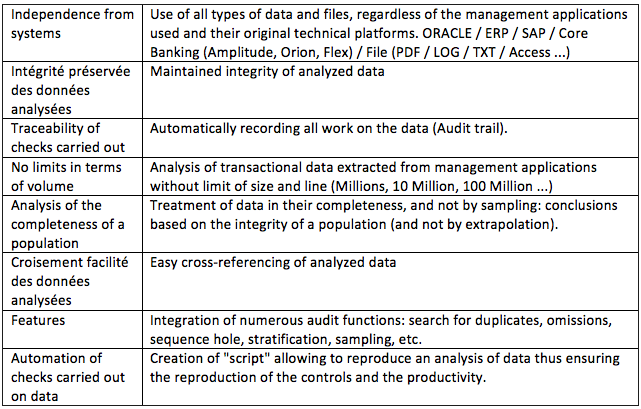
WHAT ADDED VALUE?
- Import of all types of files
- Maintained integrity of analyzed data
- File queries
- Traceability of checks carried out
- No limits in terms of volume
- Easy cross-referencing of analyzed data and files
- Automation of checks carried out on data
- Grouping of elements by category, value …
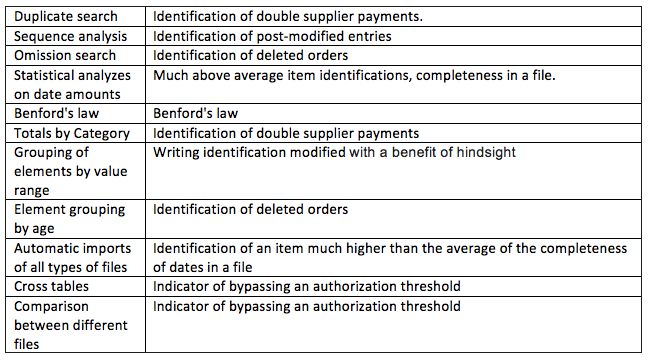
- Search for duplicates / omissions
- Log analysis
- Fraud detection
- Time saving
FOR WHICH MISSIONS ?
- Data analysis
- Data quality audit
- Fraud detection audit
WHY CASEWARE ANALYTICS ?
IDEA is a powerful and user-friendly data mining and analysis tool designed to help auditors and all financial professionals. It extends the scope of audits by detecting errors, anomalies and signs of fraud, while complying with international auditing standards. With IDEA, complex analyzes, unusual item extractions, polls, duplicate searches, and many other functions are very easy to implement thanks to its intuitive interface.
ADDED VALUE OF THE USE OF IDEA
EXAMPLES OF CONTROLS WITH IDEA
The governance of the IS is the responsibility of the directors and the board of directors. It encompasses the leadership, organizational structures and processes through which Information Technology supports and extends the strategies and objectives of the organization.
Management plans, builds, executes and monitors activities in accordance with the direction set by the governance group in order to achieve corporate objectives.
Nous vous aidons à faire l’implémentation de vos processus de gouvernance et de gestion des TI.
Any information system is part of a larger framework that requires a transversal vision to understand the assembly. In this context, the urbanization of the information system defines the main principles of siting, dismantling and construction, ensures overall consistency while reducing construction and integration costs.
Urbanization is mainly a decision support tool for controlling the IS and its transformation, for project owners and CIOs.
Our approach pursues the following objectives:
- Objective 1 : Facilitate dialogue between business actors and ICT actors, this is a sustainable intermediation
- Objective 2 : Structure the study of transformation requests, through voluntary and opportunistic action during construction projects and the implementation of new services
- Objective 3 : Support the strategic evolution of the IS
- Objective 4 : Facilitate data governance
- Objective 5 : Facilitate and simplify changes to the IS, by helping to allocate and optimize the use of resources (financial, human, data, applications, infrastructure, etc.)
- Objective 6 : Share and communicate: the approach, the knowledge of the heritage, the target and the perspectives
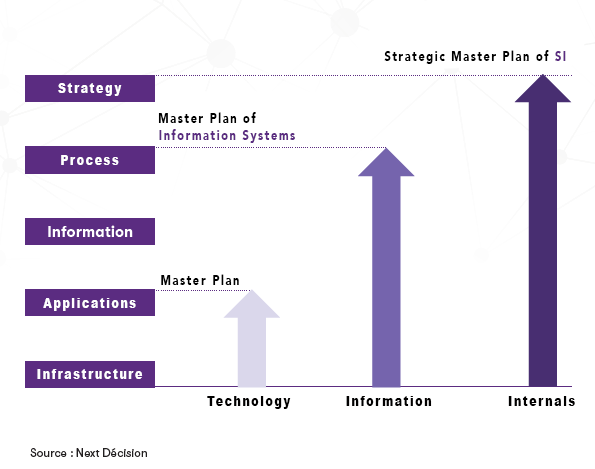
WHAT IS AN IS BLUEPRINT ?
The IS Blueprint is a document detailing the IS development strategy in accordance with the corporate strategy. It must present an existing one, a starting point: the study of needs and the definition of target systems must be made after an inventory. Objectively, the strengths and weaknesses of the organization (in terms of IT) must be mentioned during the Audit phase. This phase leads to a representation “at an instant T” of the existing IS (technical, functional, organizational architecture) then to a definition of the target.
WHAT ARE THE CHALLENGES OF THE IS BLUEPRINT ?

THE IS BLUEPRINT, FOR WHOM ?
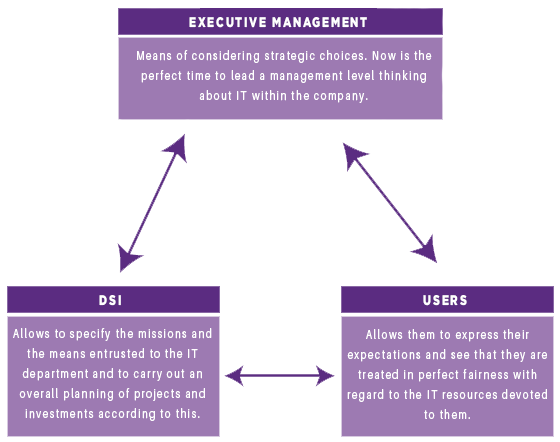
WHICH ARE THE IS BLUEPRINTS YOU NEED ?